20 KiB
Authorization
Authorization is used to check if a user is allowed to perform some specific operations in the application.
ABP extends ASP.NET Core Authorization by adding permissions as auto policies and allowing authorization system to be usable in the application services too.
So, all the ASP.NET Core authorization features and the documentation are valid in an ABP based application. This document focuses on the features that added on top of ASP.NET Core authorization features.
Authorize Attribute
ASP.NET Core defines the Authorize attribute that can be used for an action, a controller or a page. ABP allows you to use the same attribute for an application service too.
Example:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization;
using Volo.Abp.Application.Services;
namespace Acme.BookStore
{
[Authorize]
public class AuthorAppService : ApplicationService, IAuthorAppService
{
public Task<List<AuthorDto>> GetListAsync()
{
...
}
[AllowAnonymous]
public Task<AuthorDto> GetAsync(Guid id)
{
...
}
[Authorize("BookStore_Author_Create")]
public Task CreateAsync(CreateAuthorDto input)
{
...
}
}
}
Authorizeattribute forces the user to login into the application in order to use theAuthorAppServicemethods. So,GetListAsyncmethod is only available to the authenticated users.AllowAnonymoussuppresses the authentication. So,GetAsyncmethod is available to everyone including unauthorized users.[Authorize("BookStore_Author_Create")]defines a policy (see policy based authorization) that is checked to authorize the current user.
"BookStore_Author_Create" is an arbitrary policy name. If you declare an attribute like that, ASP.NET Core authorization system expects a policy to be defined before.
You can, of course, implement your policies as stated in the ASP.NET Core documentation. But for simple true/false conditions like a policy was granted to a user or not, ABP defines the permission system which will be explained in the next section.
Permission System
A permission is a simple policy that is granted or prohibited for a particular user, role or client.
Defining Permissions
To define permissions, create a class inheriting from the PermissionDefinitionProvider as shown below:
using Volo.Abp.Authorization.Permissions;
namespace Acme.BookStore.Permissions
{
public class BookStorePermissionDefinitionProvider : PermissionDefinitionProvider
{
public override void Define(IPermissionDefinitionContext context)
{
var myGroup = context.AddGroup("BookStore");
myGroup.AddPermission("BookStore_Author_Create");
}
}
}
ABP automatically discovers this class. No additional configuration required!
You typically define this class inside the
Application.Contractsproject of your application. The startup template already comes with an empty class named YourProjectNamePermissionDefinitionProvider that you can start with.
In the Define method, you first need to add a permission group or get an existing group then add permissions to this group.
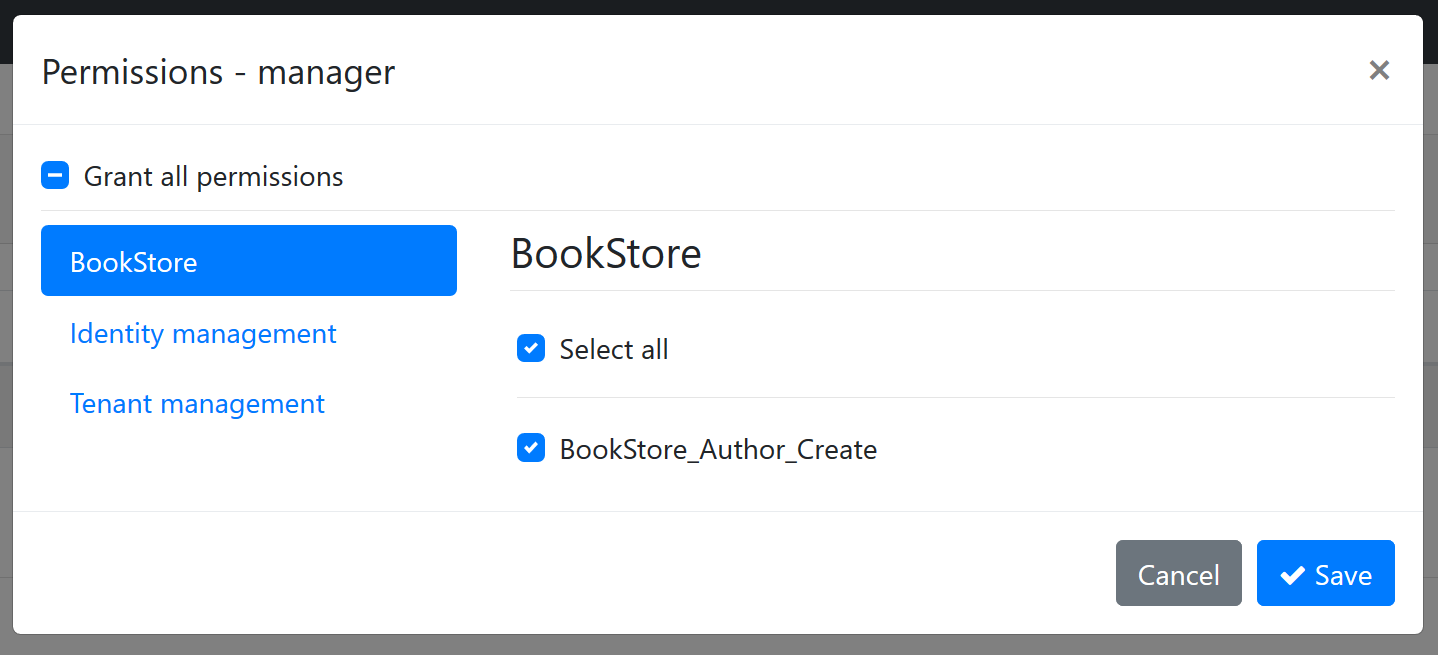
When you define a permission, it becomes usable in the ASP.NET Core authorization system as a policy name. It also becomes visible in the UI. See permissions dialog for a role:
- The "BookStore" group is shown as a new tab on the left side.
- "BookStore_Author_Create" on the right side is the permission name. You can grant or prohibit it for the role.
When you save the dialog, it is saved to the database and used in the authorization system.
The screen above is available when you have installed the identity module, which is basically used for user and role management. Startup templates come with the identity module pre-installed.
Localizing the Permission Name
"BookStore_Author_Create" is not a good permission name for the UI. Fortunately, AddPermission and AddGroup methods can take LocalizableString as second parameters:
var myGroup = context.AddGroup(
"BookStore",
LocalizableString.Create<BookStoreResource>("BookStore")
);
myGroup.AddPermission(
"BookStore_Author_Create",
LocalizableString.Create<BookStoreResource>("Permission:BookStore_Author_Create")
);
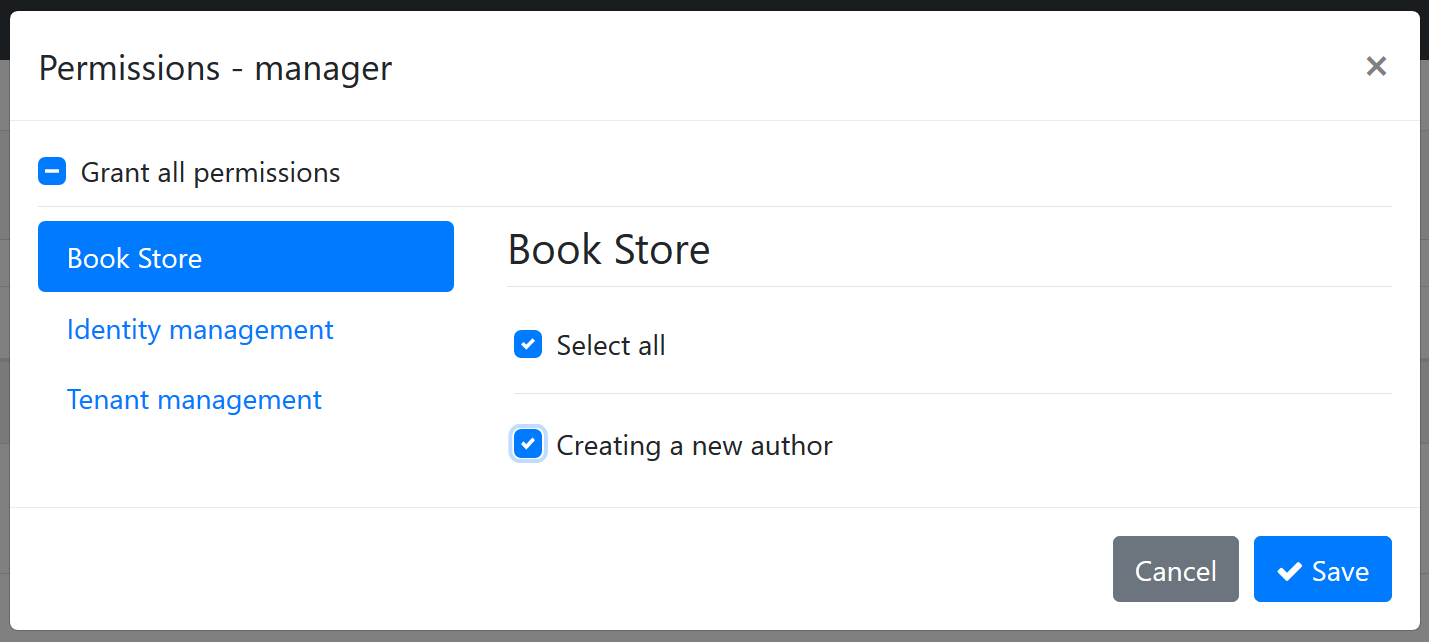
Then you can define texts for "BookStore" and "Permission:BookStore_Author_Create" keys in the localization file:
"BookStore": "Book Store",
"Permission:BookStore_Author_Create": "Creating a new author"
For more information, see the localization document on the localization system.
The localized UI will be as seen below:
Multi-Tenancy
ABP supports multi-tenancy as a first class citizen. You can define multi-tenancy side option while defining a new permission. It gets one of the three values defined below:
- Host: The permission is available only for the host side.
- Tenant: The permission is available only for the tenant side.
- Both (default): The permission is available both for tenant and host sides.
If your application is not multi-tenant, you can ignore this option.
To set the multi-tenancy side option, pass to the third parameter of the AddPermission method:
myGroup.AddPermission(
"BookStore_Author_Create",
LocalizableString.Create<BookStoreResource>("Permission:BookStore_Author_Create"),
multiTenancySide: MultiTenancySides.Tenant //set multi-tenancy side!
);
Enable/Disable Permissions
A permission is enabled by default. It is possible to disable a permission. A disabled permission will be prohibited for everyone. You can still check for the permission, but it will always return prohibited.
Example definition:
myGroup.AddPermission("Author_Management", isEnabled: false);
You normally don't need to define a disabled permission (unless you temporary want disable a feature of your application). However, you may want to disable a permission defined in a depended module. In this way you can disable the related application functionality. See the "Changing Permission Definitions of a Depended Module" section below for an example usage.
Note: Checking an undefined permission will throw an exception while a disabled permission check simply returns prohibited (false).
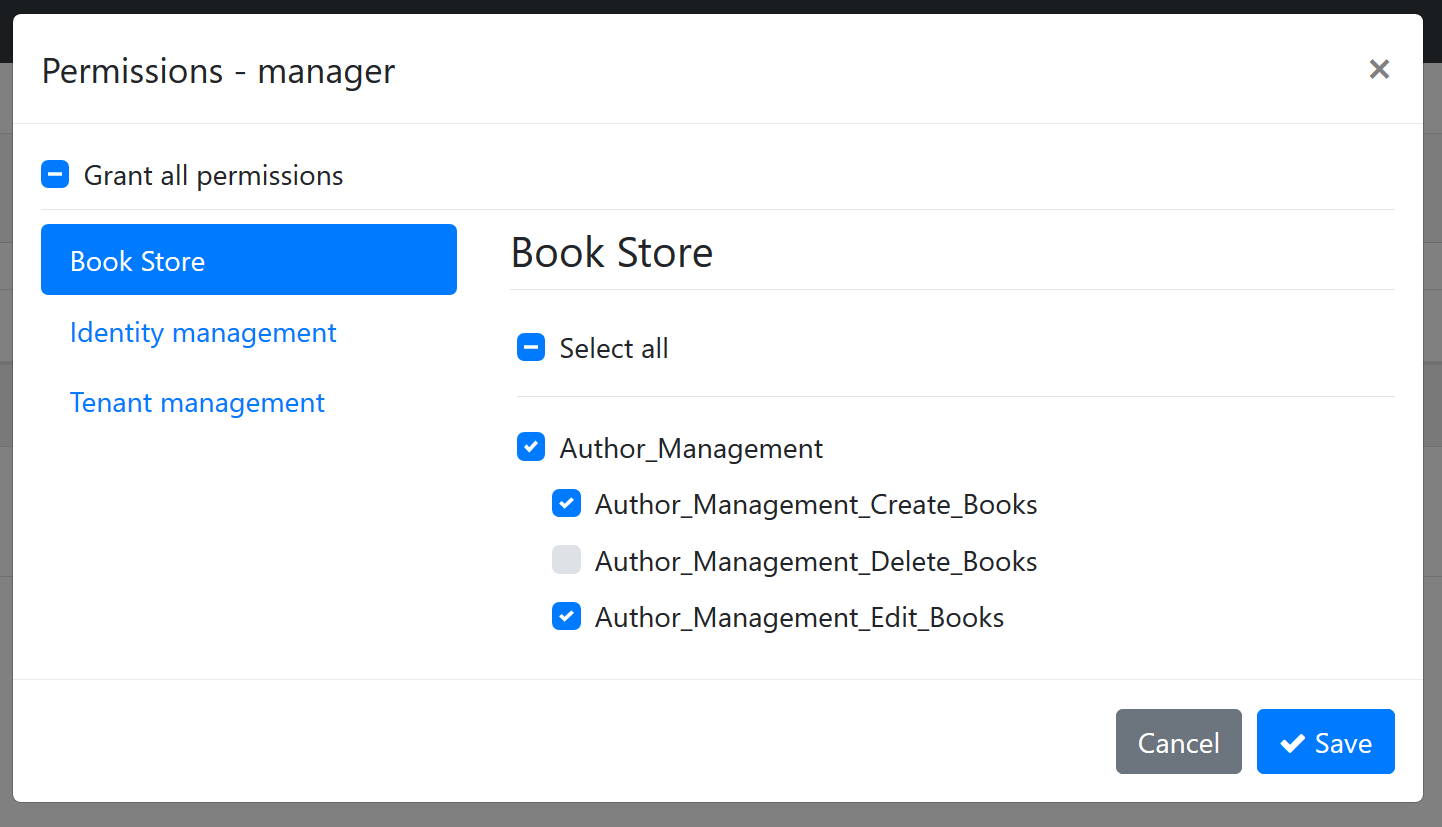
Child Permissions
A permission may have child permissions. It is especially useful when you want to create a hierarchical permission tree where a permission may have additional sub permissions which are available only if the parent permission has been granted.
Example definition:
var authorManagement = myGroup.AddPermission("Author_Management");
authorManagement.AddChild("Author_Management_Create_Books");
authorManagement.AddChild("Author_Management_Edit_Books");
authorManagement.AddChild("Author_Management_Delete_Books");
The result on the UI is shown below (you probably want to localize permissions for your application):
For the example code, it is assumed that a role/user with "Author_Management" permission granted may have additional permissions. Then a typical application service that checks permissions can be defined as shown below:
[Authorize("Author_Management")]
public class AuthorAppService : ApplicationService, IAuthorAppService
{
public Task<List<AuthorDto>> GetListAsync()
{
...
}
public Task<AuthorDto> GetAsync(Guid id)
{
...
}
[Authorize("Author_Management_Create_Books")]
public Task CreateAsync(CreateAuthorDto input)
{
...
}
[Authorize("Author_Management_Edit_Books")]
public Task UpdateAsync(CreateAuthorDto input)
{
...
}
[Authorize("Author_Management_Delete_Books")]
public Task DeleteAsync(CreateAuthorDto input)
{
...
}
}
GetListAsyncandGetAsyncwill be available to users if they haveAuthor_Managementpermission is granted.- Other methods require additional permissions.
Overriding a Permission by a Custom Policy
If you define and register a policy to the ASP.NET Core authorization system with the same name of a permission, your policy will override the existing permission. This is a powerful way to extend the authorization for a pre-built module that you are using in your application.
See policy based authorization document to learn how to define a custom policy.
Changing Permission Definitions of a Depended Module
A class deriving from the PermissionDefinitionProvider (just like the example above) can also get existing permission definitions (defined by the depended modules) and change their definitions.
Example:
context
.GetPermissionOrNull(IdentityPermissions.Roles.Delete)
.IsEnabled = false;
When you write this code inside your permission definition provider, it finds the "role deletion" permission of the Identity Module and disabled the permission, so no one can delete a role on the application.
Tip: It is better to check the value returned by the
GetPermissionOrNullmethod since it may return null if the given permission was not defined.
Permission Depending on a Condition
You may want to disable a permission based on a condition. Disabled permissions are not visible on the UI and always returns prohibited when you check them. There are two built-in conditional dependencies for a permission definition;
- A permission can be automatically disabled if a Feature was disabled.
- A permission can be automatically disabled if a Global Feature was disabled.
In addition, you can create your custom extensions.
Depending on a Features
Use the RequireFeatures extension method on your permission definition to make the permission available only if a given feature is enabled:
myGroup.AddPermission("Book_Creation")
.RequireFeatures("BookManagement");
Depending on a Global Feature
Use the RequireGlobalFeatures extension method on your permission definition to make the permission available only if a given feature is enabled:
myGroup.AddPermission("Book_Creation")
.RequireGlobalFeatures("BookManagement");
Creating a Custom Permission Dependency
PermissionDefinition supports state check, Please refer to Simple State Checker's documentation
IAuthorizationService
ASP.NET Core provides the IAuthorizationService that can be used to check for authorization. Once you inject, you can use it in your code to conditionally control the authorization.
Example:
public async Task CreateAsync(CreateAuthorDto input)
{
var result = await AuthorizationService
.AuthorizeAsync("Author_Management_Create_Books");
if (result.Succeeded == false)
{
//throw exception
throw new AbpAuthorizationException("...");
}
//continue to the normal flow...
}
AuthorizationServiceis available as a property when you derive from ABP'sApplicationServicebase class. Since it is widely used in application services,ApplicationServicepre-injects it for you. Otherwise, you can directly inject it into your class.
Since this is a typical code block, ABP provides extension methods to simplify it.
Example:
public async Task CreateAsync(CreateAuthorDto input)
{
await AuthorizationService.CheckAsync("Author_Management_Create_Books");
//continue to the normal flow...
}
CheckAsync extension method throws AbpAuthorizationException if the current user/client is not granted for the given permission. There is also IsGrantedAsync extension method that returns true or false.
IAuthorizationService has some overloads for the AuthorizeAsync method. These are explained in the ASP.NET Core authorization documentation.
Tip: Prefer to use the
Authorizeattribute wherever possible, since it is declarative & simple. UseIAuthorizationServiceif you need to conditionally check a permission and run a business code based on the permission check.
Check a Permission in JavaScript
See the following documents to learn how to re-use the authorization system on the client side:
Permission Management
Permission management is normally done by an admin user using the permission management modal:
If you need to manage permissions by code, inject the IPermissionManager and use as shown below:
public class MyService : ITransientDependency
{
private readonly IPermissionManager _permissionManager;
public MyService(IPermissionManager permissionManager)
{
_permissionManager = permissionManager;
}
public async Task GrantPermissionForUserAsync(Guid userId, string permissionName)
{
await _permissionManager.SetForUserAsync(userId, permissionName, true);
}
public async Task ProhibitPermissionForUserAsync(Guid userId, string permissionName)
{
await _permissionManager.SetForUserAsync(userId, permissionName, false);
}
}
SetForUserAsync sets the value (true/false) for a permission of a user. There are more extension methods like SetForRoleAsync and SetForClientAsync.
IPermissionManager is defined by the permission management module. See the permission management module documentation for more information.
Advanced Topics
Permission Value Providers
Permission checking system is extensible. Any class derived from PermissionValueProvider (or implements IPermissionValueProvider) can contribute to the permission check. There are three pre-defined value providers:
UserPermissionValueProviderchecks if the current user is granted for the given permission. It gets user id from the current claims. User claim name is defined with theAbpClaimTypes.UserIdstatic property.RolePermissionValueProviderchecks if any of the roles of the current user is granted for the given permission. It gets role names from the current claims. Role claims name is defined with theAbpClaimTypes.Rolestatic property.ClientPermissionValueProviderchecks if the current client is granted for the given permission. This is especially useful on a machine to machine interaction where there is no current user. It gets the client id from the current claims. Client claim name is defined with theAbpClaimTypes.ClientIdstatic property.
You can extend the permission checking system by defining your own permission value provider.
Example:
public class SystemAdminPermissionValueProvider : PermissionValueProvider
{
public SystemAdminPermissionValueProvider(IPermissionStore permissionStore)
: base(permissionStore)
{
}
public override string Name => "SystemAdmin";
public async override Task<PermissionGrantResult>
CheckAsync(PermissionValueCheckContext context)
{
if (context.Principal?.FindFirst("User_Type")?.Value == "SystemAdmin")
{
return PermissionGrantResult.Granted;
}
return PermissionGrantResult.Undefined;
}
}
This provider allows for all permissions to a user with a User_Type claim that has SystemAdmin value. It is common to use current claims and IPermissionStore in a permission value provider.
A permission value provider should return one of the following values from the CheckAsync method:
PermissionGrantResult.Grantedis returned to grant the user for the permission. If any of the providers returnGranted, the result will beGranted, if no other provider returnsProhibited.PermissionGrantResult.Prohibitedis returned to prohibit the user for the permission. If any of the providers returnProhibited, the result will always beProhibited. Doesn't matter what other providers return.PermissionGrantResult.Undefinedis returned if this value provider could not decide about the permission value. Return this to let other providers check the permission.
Once a provider is defined, it should be added to the AbpPermissionOptions as shown below:
Configure<AbpPermissionOptions>(options =>
{
options.ValueProviders.Add<SystemAdminPermissionValueProvider>();
});
Permission Store
IPermissionStore is the only interface that needs to be implemented to read the value of permissions from a persistence source, generally a database system. The Permission Management module implements it and pre-installed in the application startup template. See the permission management module documentation for more information
AlwaysAllowAuthorizationService
AlwaysAllowAuthorizationService is a class that is used to bypass the authorization service. It is generally used in integration tests where you may want to disable the authorization system.
Use IServiceCollection.AddAlwaysAllowAuthorization() extension method to register the AlwaysAllowAuthorizationService to the dependency injection system:
public override void ConfigureServices(ServiceConfigurationContext context)
{
context.Services.AddAlwaysAllowAuthorization();
}
This is already done for the startup template integration tests.
Claims Principal Factory
Claims are important elements of authentication and authorization. ABP uses the IAbpClaimsPrincipalFactory service to create claims on authentication. This service was designed as extensible. If you need to add your custom claims to the authentication ticket, you can implement the IAbpClaimsPrincipalContributor in your application.
Example: Add a SocialSecurityNumber claim:
public class SocialSecurityNumberClaimsPrincipalContributor : IAbpClaimsPrincipalContributor, ITransientDependency
{
public async Task ContributeAsync(AbpClaimsPrincipalContributorContext context)
{
var identity = context.ClaimsPrincipal.Identities.FirstOrDefault();
var userId = identity?.FindUserId();
if (userId.HasValue)
{
var userService = context.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<IUserService>(); //Your custom service
var socialSecurityNumber = await userService.GetSocialSecurityNumberAsync(userId.Value);
if (socialSecurityNumber != null)
{
identity.AddClaim(new Claim("SocialSecurityNumber", socialSecurityNumber));
}
}
}
}