8.7 KiB
Getting Started
//[doc-params]
{
"UI": ["MVC", "Blazor", "BlazorServer", "NG"],
"DB": ["EF", "Mongo"],
"Tiered": ["Yes", "No"]
}
This document assumes that you prefer to use {{ UI_Value }} as the UI framework and {{ DB_Value }} as the database provider. For other options, please change the preference on top of this document.
Create the Database
Connection String
Check the connection string in the appsettings.json file under the {{if Tiered == "Yes"}}.IdentityServer and .HttpApi.Host projects{{else}}{{if UI=="MVC"}}.Web project{{else if UI=="BlazorServer"}}.Blazor project{{else}}.HttpApi.Host project{{end}}{{end}}.
{{ if DB == "EF" }}
"ConnectionStrings": {
"Default": "Server=(LocalDb)\MSSQLLocalDB;Database=BookStore;Trusted_Connection=True"
}
About the Connection Strings and Database Management Systems
The solution is configured to use Entity Framework Core with MS SQL Server by default. However, if you've selected another DBMS using the
-dbmsparameter on the ABP CLInewcommand (like-dbms MySQL), the connection string might be different for you.EF Core supports various database providers and you can use any supported DBMS. See the Entity Framework integration document to learn how to switch to another DBMS if you need later.
Database Migrations
The solution uses the Entity Framework Core Code First Migrations. It comes with a .DbMigrator console application which applies the migrations and also seeds the initial data. It is useful on development as well as on production environment.
.DbMigratorproject has its ownappsettings.json. So, if you have changed the connection string above, you should also change this one.
The Initial Migration
.DbMigrator application automatically creates the Initial migration on first run.
If you are using Visual Studio, you can skip to the Running the DbMigrator section. However, other IDEs (e.g. Rider) may have problems for the first run since it adds the initial migration and compiles the project. In this case, open a command line terminal in the folder of the .DbMigrator project and run the following command:
dotnet run
For the next time, you can just run it in your IDE as you normally do.
Running the DbMigrator
Right click to the .DbMigrator project and select Set as StartUp Project
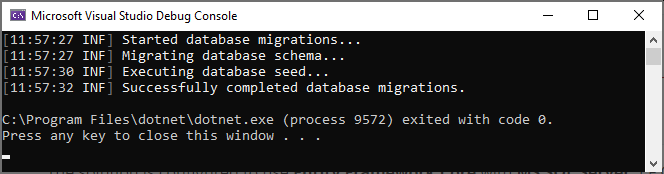
Hit F5 (or Ctrl+F5) to run the application. It will have an output like shown below:
Initial seed data creates the
adminuser in the database (with the password is1q2w3E*) which is then used to login to the application. So, you need to use.DbMigratorat least once for a new database.
{{ else if DB == "Mongo" }}
"ConnectionStrings": {
"Default": "mongodb://localhost:27017/BookStore"
}
The solution is configured to use MongoDB in your local computer, so you need to have a MongoDB server instance up and running or change the connection string to another MongoDB server.
Seed Initial Data
The solution comes with a .DbMigrator console application which seeds the initial data. It is useful on development as well as on production environment.
.DbMigratorproject has its ownappsettings.json. So, if you have changed the connection string above, you should also change this one.
Right click to the .DbMigrator project and select Set as StartUp Project
Hit F5 (or Ctrl+F5) to run the application. It will have an output like shown below:
Initial seed data creates the
adminuser in the database (with the password is1q2w3E*) which is then used to login to the application. So, you need to use.DbMigratorat least once for a new database.
{{ end }}
Run the Application
{{ if UI == "MVC" || UI == "BlazorServer" }}
{{ if Tiered == "Yes" }}
Tiered solutions use Redis as the distributed cache. Ensure that it is installed and running in your local computer. If you are using a remote Redis Server, set the configuration in the
appsettings.jsonfiles of the projects below.
- Ensure that the
.IdentityServerproject is the startup project. Run this application that will open a login page in your browser.
Use Ctrl+F5 in Visual Studio (instead of F5) to run the application without debugging. If you don't have a debug purpose, this will be faster.
You can login, but you cannot enter to the main application here. This is just the authentication server.
- Ensure that the
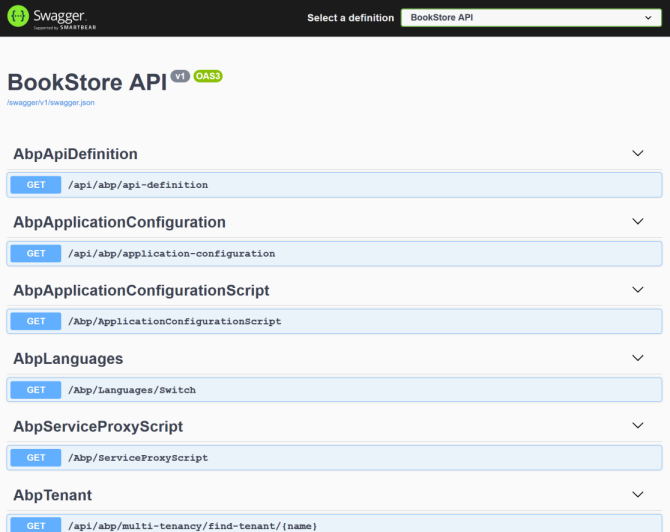
.HttpApi.Hostproject is the startup project and run the application which will open a Swagger UI in your browser.
This is the HTTP API that is used by the web application.
- Lastly, ensure that the {{if UI=="MVC"}}
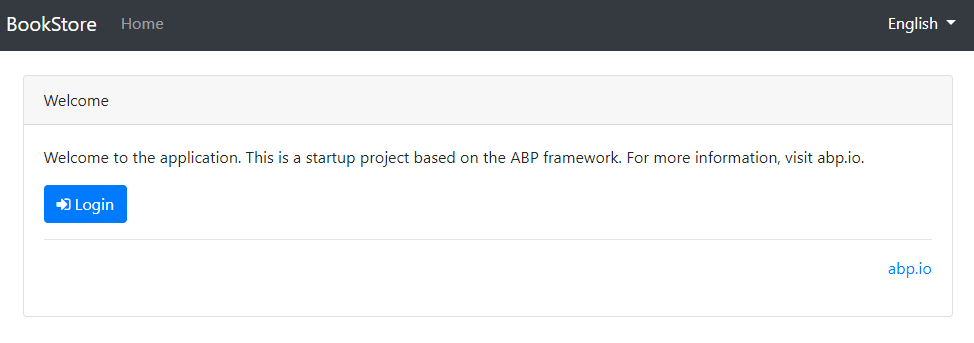
.Web{{else}}.Blazor{{end}} project is the startup project and run the application which will open a welcome page in your browser
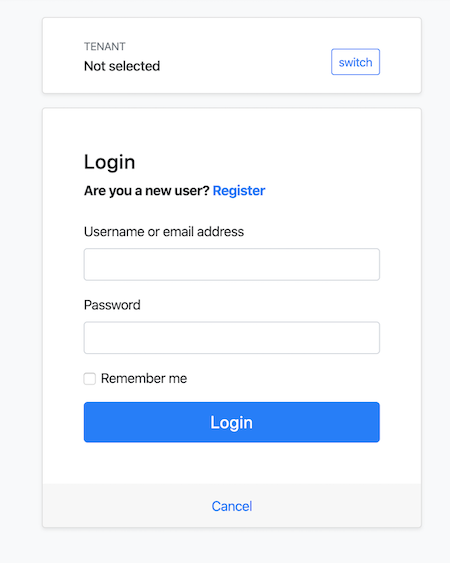
Click to the login button which will redirect you to the authentication server to login to the application:
{{ else # Tiered != "Yes" }}
Ensure that the {{if UI=="MVC"}}.Web{{else}}.Blazor{{end}} project is the startup project. Run the application which will open the login page in your browser:
Use Ctrl+F5 in Visual Studio (instead of F5) to run the application without debugging. If you don't have a debug purpose, this will be faster.
{{ end # Tiered }}
{{ else # UI != MVC || BlazorServer }}
Running the HTTP API Host (Server Side)
{{ if Tiered == "Yes" }}
Tiered solutions use Redis as the distributed cache. Ensure that it is installed and running in your local computer. If you are using a remote Redis Server, set the configuration in the
appsettings.jsonfiles of the projects below.
Ensure that the .IdentityServer project is the startup project. Run the application which will open a login page in your browser.
Use Ctrl+F5 in Visual Studio (instead of F5) to run the application without debugging. If you don't have a debug purpose, this will be faster.
You can login, but you cannot enter to the main application here. This is just the authentication server.
Ensure that the .HttpApi.Host project is the startup project and run the application which will open a Swagger UI:
{{ else # Tiered == "No" }}
Ensure that the .HttpApi.Host project is the startup project and run the application which will open a Swagger UI:
Use Ctrl+F5 in Visual Studio (instead of F5) to run the application without debugging. If you don't have a debug purpose, this will be faster.
{{ end # Tiered }}
You can see the application APIs and test them here. Get more info about the Swagger UI.
{{ end # UI }}
{{ if UI == "Blazor" }}
Running the Blazor Application (Client Side)
Ensure that the .Blazor project is the startup project and run the application.
Use Ctrl+F5 in Visual Studio (instead of F5) to run the application without debugging. If you don't have a debug purpose, this will be faster.
Once the application starts, click to the Login link on to header, which redirects you to the authentication server to enter a username and password:
{{ else if UI == "NG" }}
Running the Angular Application (Client Side)
Go to the angular folder, open a command line terminal, type the yarn command (we suggest to the yarn package manager while npm install will also work)
yarn
Once all node modules are loaded, execute yarn start (or npm start) command:
yarn start
It may take a longer time for the first build. Once it finishes, it opens the Angular UI in your default browser with the localhost:4200 address.
{{ end }}
Enter admin as the username and 1q2w3E* as the password to login to the application. The application is up and running. You can start developing your application based on this startup template.