# ASP.NET Core MVC / Razor Pages UI: Modals
While you can continue to use the standard [Bootstrap way](https://getbootstrap.com/docs/4.5/components/modal/) to create, open and manage modals in your applications, ABP Framework provides a **flexible** way to manage modals by **automating common tasks** for you.
**Example: A modal dialog to create a new role entity**
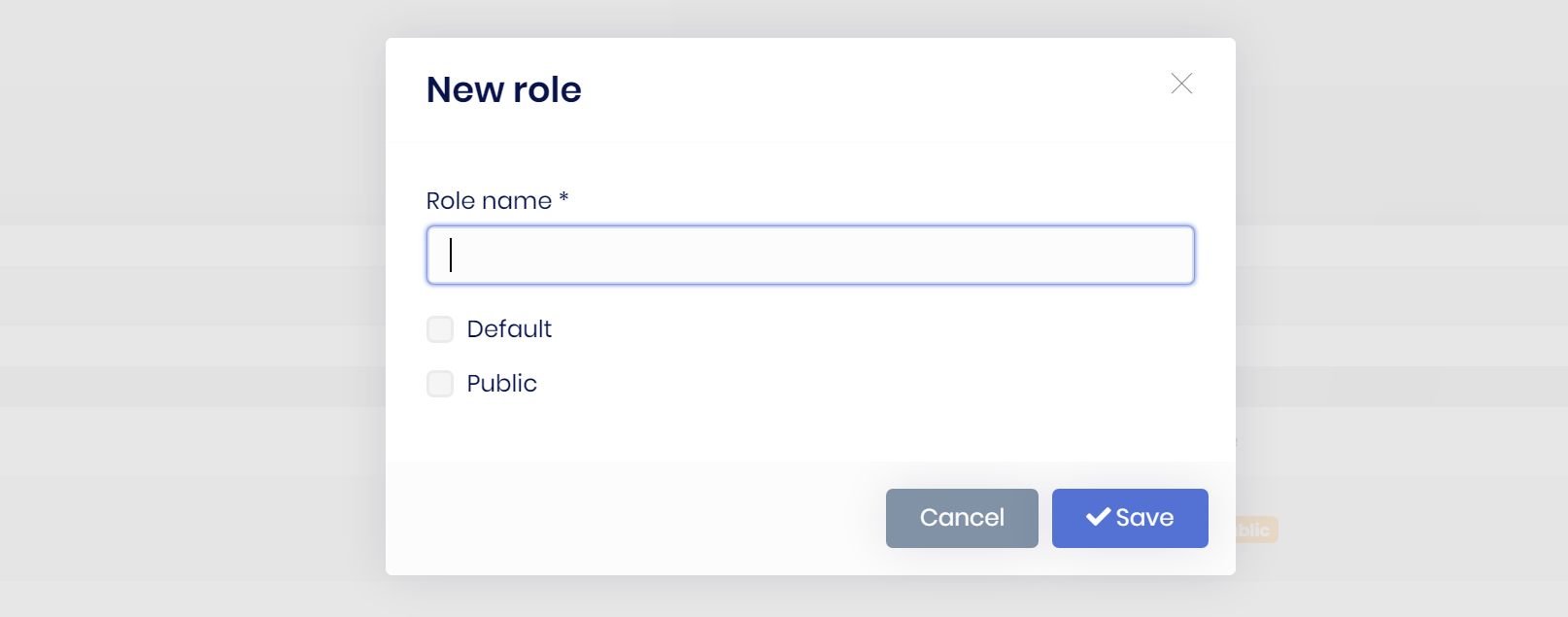
ABP Framework provides the following benefits for such a modal with a form inside it;
* **Lazy loads** the modal HTML into the page and **removes** it from the DOM once its closed. This makes easy to consume a reusable modal dialog. Also, every time you open the modal, it will be a fresh new modal, so you don't have to deal with resetting the modal content.
* **Auto-focuses** the first input of the form once the modal has been opened.
* Automatically determines the **form** inside a modal and posts the form via **AJAX** instead of normal page post.
* Automatically checks if the form inside the modal **has changed, but not saved**. It warns the user in this case.
* Automatically **disables the modal buttons** (save & cancel) until the AJAX operation completes.
* Makes it easy to register a **JavaScript object that is initialized** once the modal has loaded.
So, it makes you write less code when you deal with the modals, especially the modals with a form inside.
## Basic Usage
### Creating a Modal as a Razor Page
To demonstrate the usage, we are creating a simple Razor Page, named `ProductInfoModal.cshtml`, under the `/Pages/Products` folder:
**ProductInfoModal.cshtml Content:**
````html
@page
@model MyProject.Web.Pages.Products.ProductInfoModalModel
@{
Layout = null;
}
@Model.ProductName
@Model.ProductDescription
Reference: https://acme.com/catalog/
````
* This page sets the `Layout` to `null` since we will show this as a modal. So, no need to wrap with a layout.
* It uses [abp-modal tag helper](Tag-Helpers/Modals.md) to simplify creating the modal HTML code. You can use the standard Bootstrap modal code if you prefer it.
**ProductInfoModalModel.cshtml.cs Content:**
```csharp
using Volo.Abp.AspNetCore.Mvc.UI.RazorPages;
namespace MyProject.Web.Pages.Products
{
public class ProductInfoModalModel : AbpPageModel
{
public string ProductName { get; set; }
public string ProductDescription { get; set; }
public string ProductImageUrl { get; set; }
public void OnGet()
{
ProductName = "Acme Indestructo Steel Ball";
ProductDescription = "The ACME Indestructo Steel Ball is completely indestructible, there is nothing that can destroy it!";
ProductImageUrl = "https://acme.com/catalog/acmeindestructo.jpg";
}
}
}
```
You can surely get the product info from a database or API. We are setting the properties hard-coded for the sake of simplicity,
### Defining the Modal Manager
Once you have a modal, you can open it in any page using some simple **JavaScript** code.
First, create an `abp.ModalManager` object by setting the `viewUrl`, in the JavaScript file of the page that will use the modal:
````js
var productInfoModal = new abp.ModalManager({
viewUrl: '/Products/ProductInfoModal'
});
````
> If you only need to specify the `viewUrl`, you can directly pass it to the `ModalManager` constructor, as a shortcut. Example: `new abp.ModalManager('/Products/ProductInfoModal');`
### Opening the Modal
Then open the modal whenever you need:
````js
productInfoModal.open();
````
You typically want to open the modal when something happens; For example, when the user clicks a button:
````js
$('#OpenProductInfoModal').click(function(){
productInfoModal.open();
});
````
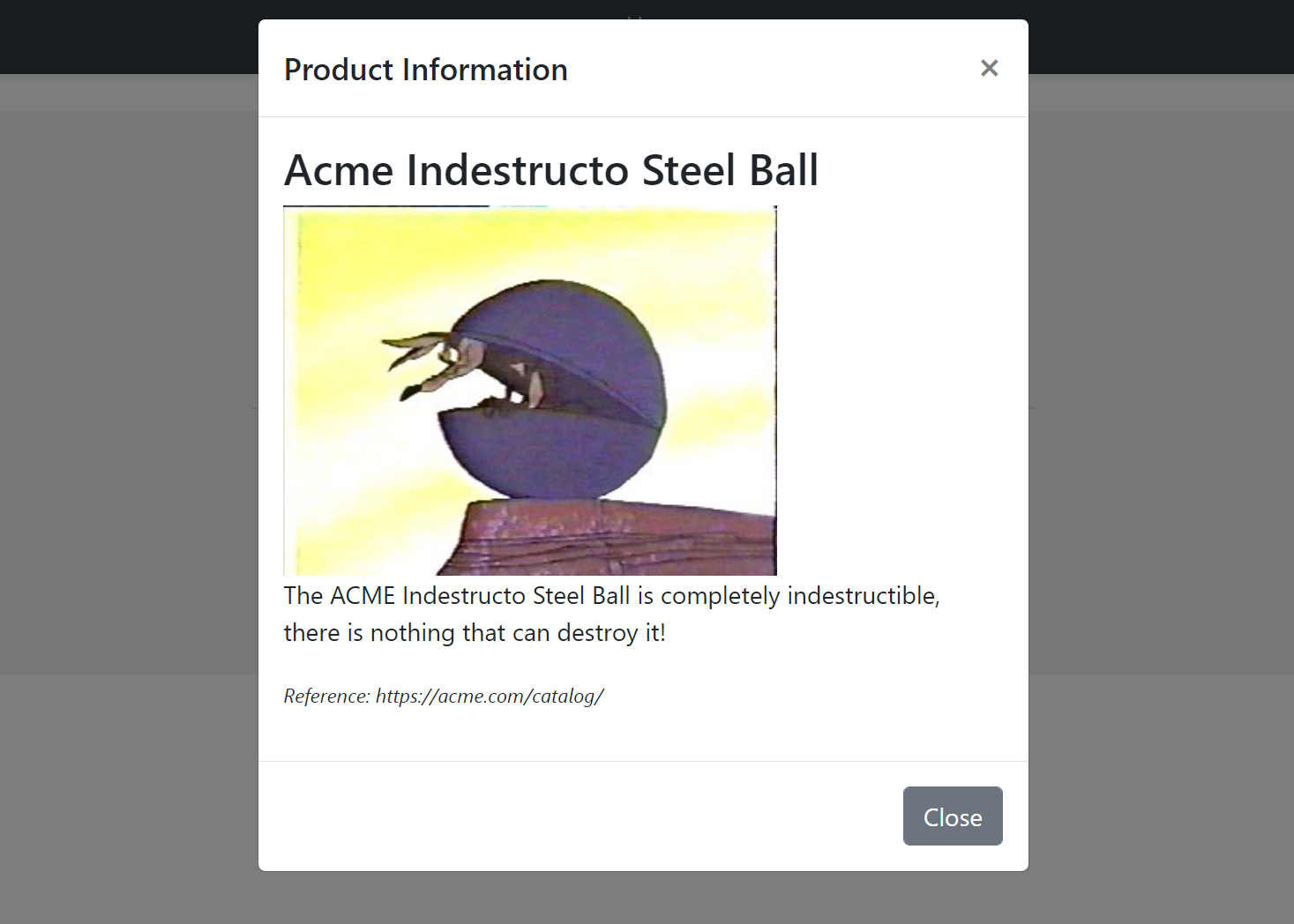
The resulting modal will be like that:
#### Opening the Modal with Arguments
When you call the `open()` method, `ModalManager` loads the modal HTML by requesting it from the `viewUrl`. You can pass some **query string parameters** to this URL when you open the modal.
**Example: Pass the product id while opening the modal**
````js
productInfoModal.open({
productId: 42
});
````
You can add a `productId` parameter to the get method:
````csharp
using Volo.Abp.AspNetCore.Mvc.UI.RazorPages;
namespace MyProject.Web.Pages.Products
{
public class ProductInfoModalModel : AbpPageModel
{
//...
public async Task OnGetAsync(int productId) //Add productId parameter
{
//TODO: Get the product with database with the given productId
//...
}
}
}
````
In this way, you can use the `productId` to query the product from a data source.
## Modals with Forms
`abp.ModalManager` handles various common tasks (described in the introduction) when you want to use a form inside the modal.
### Example Modal with a Form
This section shows an example form to create a new product.
#### Creating the Razor Page
For this example, creating a new Razor Page, named `ProductCreateModal.cshtml`, under the `/Pages/Products` folder:

**ProductCreateModal.cshtml Content:**
````html
@page
@using Volo.Abp.AspNetCore.Mvc.UI.Bootstrap.TagHelpers.Modal
@model MyProject.Web.Pages.Products.ProductCreateModalModel
@{
Layout = null;
}
````
* The `abp-modal` has been wrapped by the `form`. This is needed to place the `Save` and the `Cancel` buttons into the form. In this way, the `Save` button acts as the `submit` button for the `form`.
* Used the [abp-input tag helpers](Tag-Helpers/Form-Elements.md) to simplify to create the form elements. Otherwise, you need to write more HTML.
**ProductCreateModal.cshtml.cs Content:**
```csharp
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Volo.Abp.AspNetCore.Mvc.UI.RazorPages;
namespace MyProject.Web.Pages.Products
{
public class ProductCreateModalModel : AbpPageModel
{
[BindProperty]
public PoductCreationDto Product { get; set; }
public async Task OnGetAsync()
{
//TODO: Get logic, if available
}
public async Task OnPostAsync()
{
//TODO: Save the Product...
return NoContent();
}
}
}
```
* This is a simple `PageModal` class. The `[BindProperty]` make the form binding to the model when you post (submit) the form; The standard ASP.NET Core system.
* `OnPostAsync` returns `NoContent` (this method is defined by the base `AbpPageModel` class). Because we don't need to a return value in the client side, after the form post operation.
**PoductCreationDto:**
`ProductCreateModalModel` uses a `PoductCreationDto` class defined as shown below:
````csharp
using System;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using Volo.Abp.AspNetCore.Mvc.UI.Bootstrap.TagHelpers.Form;
namespace MyProject.Web.Pages.Products
{
public class PoductCreationDto
{
[Required]
[StringLength(128)]
public string Name { get; set; }
[TextArea(Rows = 4)]
[StringLength(2000)]
public string Description { get; set; }
[DataType(DataType.Date)]
public DateTime ReleaseDate { get; set; }
}
}
````
* `abp-input` Tag Helper can understand the data annotation attributes and uses them to shape and validate the form elements. See the [abp-input tag helpers](Tag-Helpers/Form-Elements.md) document to learn more.
#### Defining the Modal Manager
Again, create an `abp.ModalManager` object by setting the `viewUrl`, in the JavaScript file of the page that will use the modal:
````js
var productCreateModal = new abp.ModalManager({
viewUrl: '/Products/ProductCreateModal'
});
````
#### Opening the Modal
Then open the modal whenever you need:
````js
productCreateModal.open();
````
You typically want to open the modal when something happens; For example, when the user clicks a button:
````js
$('#OpenProductCreateModal').click(function(){
productCreateModal.open();
});
````
So, the complete code will be something like that (assuming you have a `button` with `id` is `OpenProductCreateModal` on the view side):
```js
$(function () {
var productCreateModal = new abp.ModalManager({
viewUrl: '/Products/ProductCreateModal'
});
$('#OpenProductCreateModal').click(function () {
productCreateModal.open();
});
});
```
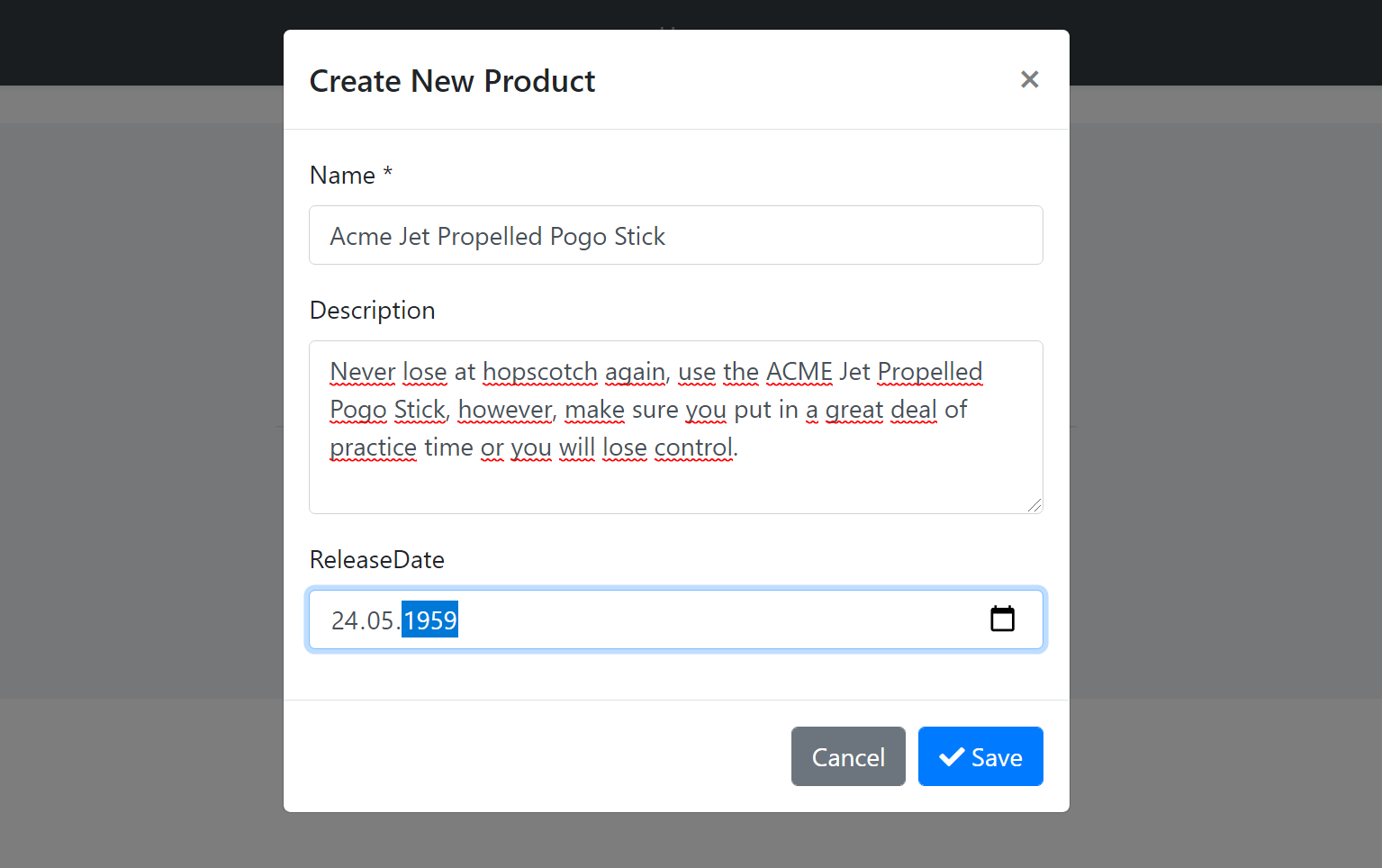
The resulting modal will be like that:
#### Saving the Modal
When you click to the `Save` button, the form is posted to the server. If the server returns a **success response**, then the `onResult` event is triggered with some arguments including the server response and the modal is automatically closed.
An example callback that logs the arguments passed to the `onResult` method:
````js
productCreateModal.onResult(function(){
console.log(arguments);
});
````
If the server returns a failed response, it shows the error message returned from the server and keeps the modal open.
> See the *Modal Manager Reference* section below for other modal events.
#### Canceling the Modal
If you click to the Cancel button with some changes made but not saved, you get such a warning message:
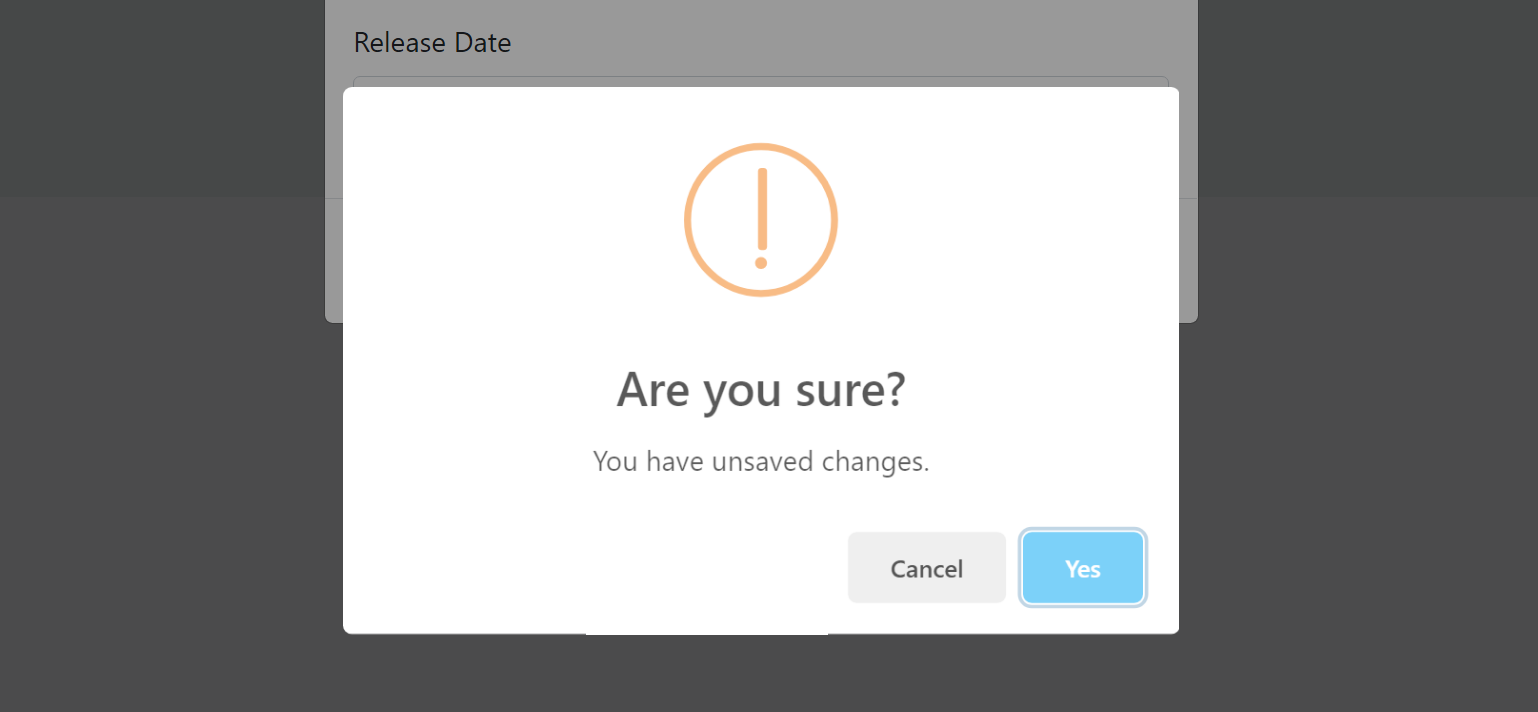
If you don't want such a check & message, you can add `data-check-form-on-close="false"` attribute to your `form` element. Example:
````html