# ASP.NET Core MVC / Razor Pages: Forms & Validation
ABP Framework provides infrastructure and conventions to make easier to create forms, localize display names for the form elements and handle server & client side validation;
* [abp-dynamic-form](Tag-Helpers/Dynamic-Forms.md) tag helper automates **creating a complete form** from a C# model class: Creates the input elements, handles localization and client side validation.
* [ABP Form tag helpers](Tag-Helpers/Form-elements.md) (`abp-input`, `abp-select`, `abp-radio`...) render **a single form element** with handling localization and client side validation.
* ABP Framework automatically **localizes the display name** of a form element without needing to add a `[DisplayName]` attribute.
* **Validation errors** are automatically localized based on the user culture.
> This document is for the **client side validation** and it doesn't cover the server side validation. Check the [validation document](../../Validation.md) for server side validation infrastructure.
## The Classic Way
In a typical Bootstrap based ASP.NET Core MVC / Razor Pages UI, you [need to write](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/mvc/models/validation#client-side-validation) such a boilerplate code to create a simple form element:
````html
````
You can continue to use this approach if you need or prefer it. However, ABP Form tag helpers can produce the same output with a minimal code.
## ABP Dynamic Forms
[abp-dynamic-form](Tag-Helpers/Dynamic-Forms.md) tag helper completely automates the form creation. Take this model class as an example:
```csharp
using System;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using Volo.Abp.AspNetCore.Mvc.UI.Bootstrap.TagHelpers.Form;
namespace MyProject.Web.Pages
{
public class MovieViewModel
{
[Required]
[StringLength(256)]
public string Name { get; set; }
[Required]
[DataType(DataType.Date)]
public DateTime ReleaseDate { get; set; }
[Required]
[TextArea]
[StringLength(1000)]
public string Description { get; set; }
public Genre Genre { get; set; }
public float? Price { get; set; }
public bool PreOrder { get; set; }
}
}
```
It uses the data annotation attributes to define validation rules and UI styles for the properties. `Genre`, is an `enum` in this example:
````csharp
namespace MyProject.Web.Pages
{
public enum Genre
{
Classic,
Action,
Fiction,
Fantasy,
Animation
}
}
````
In order to create the form in a razor page, create a property in your `PageModel` class:
```csharp
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
namespace MyProject.Web.Pages
{
public class CreateMovieModel : PageModel
{
[BindProperty]
public MovieViewModel Movie { get; set; }
public void OnGet()
{
Movie = new MovieViewModel();
}
public async Task OnPostAsync()
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
//TODO: Save the Movie
}
}
}
}
```
Then you can render the form in the `.cshtml` file:
```html
@page
@model MyProject.Web.Pages.CreateMovieModel
Create a new Movie
```
The result is shown below:

See the *Localization & Validation* section below to localize the field display names and see how the validation works.
> See [its own document](Tag-Helpers/Dynamic-Forms.md) for all options of the `abp-dynamic-form` tag helper.
## ABP Form Tag Helpers
`abp-dynamic-form` covers most of the scenarios and allows you to control and customize the form using the attributes.
However, if you want to **render the form body yourself** (for example, you may want to fully control the **form layout**), you can directly use the [ABP Form Tag Helpers](Tag-Helpers/Form-elements.md). The same auto-generated form above can be created using the ABP Form Tag Helpers as shown below:
```html
@page
@model MyProject.Web.Pages.CreateMovieModel
Create a new Movie
```
> See the [ABP Form Tag Helpers](Tag-Helpers/Form-elements.md) document for details of these tag helpers and their options.
## Validation & Localization
Both of the Dynamic Form and the Form Tag Helpers **automatically validate** the input based on the data annotation attributes and shows validation error messages on the user interface. Error messages are **automatically localized** based on the current culture.
**Example: User leaves empty a required string property**
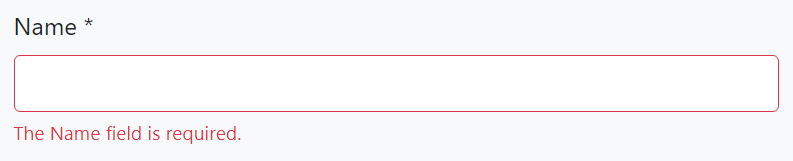
The error message below is shown if the language is French:

Validation errors are already [translated](https://github.com/abpframework/abp/tree/dev/framework/src/Volo.Abp.Validation/Volo/Abp/Validation/Localization) a lot of languages. You can [contribute](../../Contribution/Index.md) to the translation for your own language or override the texts for your own application by following the [localization](../../Localization.md) documentation.
## Display Name Localization
ABP Framework uses the property name as the field name on the user interface. You typically want to [localize](../../Localization.md) this name based on the current culture.
ABP Framework can conventionally localize the fields on the UI when you add the localization keys to the localization JSON files.
Example: French localization for the *Name* property (add into the `fr.json` in the application):
````js
"Name": "Nom"
````
Then the UI will use the given name for French language:
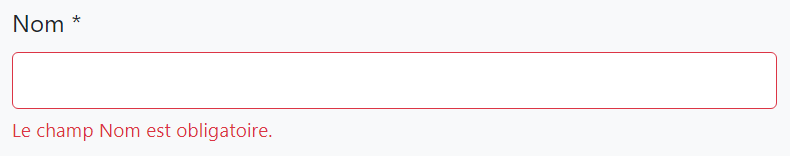
### Using the `DisplayName:` Prefix
Directly using the property name as the localization key may be a problem if you need to use the property name for other purpose, which a different translation value. In this case, use the `DisplayName:` prefix for the localization key:
````js
"DisplayName:Name": "Nom"
````
ABP prefers to use the `DisplayName:Name` key over the `Name` key if it does exists.
### Using a Custom Localization Key
If you need, you can use the `[DisplayName]` attribute to specify the localization key for a specific property:
````csharp
[DisplayName("MyNameKey")]
public string Name { get; set; }
````
In this case, you can add an entry to the localization file using the key `MyNameKey`.
> If you use the `[DisplayName]` but not add a corresponding entity to the localization file, then ABP Framework shows the given key as the field name, `MyNameKey` for this case. So, it provides a way to specify a hard coded display name even if you don't need to use the localization system.
## See Also
* [Server Side Validation](../../Validation.md)